 |
The Algorand Blockchain
Last Reviewed: December 2022
I'll run through the basics of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology to begin with. That means you won't need to be too familiar with cryptocurrency in order for this article to make sense. If it feels too daunting to tackle right now, then maybe have a look at my Beginners Guide to Algorand first.
If you're already familiar with the world of cryptocurrencies I suggest you skip ahead to the latter half of the article where I specifically talk about how the Algorand blockchain technology works and then compare Algorand vs Bitcoin.
With that said, let's cut to the chase and get right to it.
Recommended Article:
What is a Blockchain?
A cryptocurrency is a digital currency that's hosted on a blockchain. The blockchain is actually what makes a given cryptocurrency unique and provides the currency (or token) with its traits. The blockchain is essentially a ledger that is distributed to every connected computer in the network. Different blockchains works differently, but the main defining principle is that it's decentralized - everyone in the network holds a copy of the ledger. It's important that the information in these ledgers are identical to one another. This system makes crypto very resistant to tampering and counterfeit.
The Blockchain Book Metaphor
You can fundamentally think of the blockchain ledger as an accounting book that contains all the information about a particular blockchain network. Everyone who uses this blockchain network has a copy of the book. Every transaction ever made (and all the information related to it) must be stored in this book. This means that every time a transaction is made there must be a new line of text in the book to record it. In addition, this line of text must be written into every. single. book.
This works fine and dandy if it's just you and a couple friends owning a company together and accounting for your daily sales, and maybe only selling a few items every hour. However, that's not the case for cryptocurrencies, as there needs to be support for thousands of transactions every second, and millions of books need to have every transaction recorded into them. You're probably starting to see the problem here.
So, in order to have a functioning system we need everyone in the network to write the exact same information in the book, in the exact same order, at the same time, without allowing for any fraudulent writings on the ledger (meaning it has to be scalable & secure). It's also insufficient if we write too slowly, only allowing for a limited number of transactions per second. A slow writing system would lead to transactions queuing up and thus cause slow transaction speeds. Hence speed is of importance.
It's easy to see how running a complex system like this can become expensive, and this would usually reflect in the transaction costs on a given blockchain.
Bitcoin - The First Blockchain
Bitcoin (BTC) was launched in 2009 and was the first cryptocurrency that took advantage using this blockchain technology. It was revolutionary in itself, but the technology is starting to show it's age. Several competitors have launched their own blockchains in the recent years by refining these essential aspects mentioned above (speed, scalability, security, cost). The actual cryptocurrency is just the token that's supported by a given blockchain, which can be used as a medium for exchange and trade.
Bitcoins blockchain protocol uses a cryptographic system known as Proof-of-Work (PoW). Shortly summarized computers are used to solve highly complex mathematical problems. Whoever solves a mathematical problem in turn gets the right to create and verify the next entry (known as block) into the blockchain ledger, and for this work they are rewarded with some BTC. In this way everyone who contributes with computer power have a chance of solving the next block in the chain (hence the term blockchain). As such the network is decentralized among many participants.
There is of course a bit more to it, and different blockchains have different technical solutions, but that's all you need to know for now.
What is the Algorand Blockchain?
Algorand is a blockchain that was launched in April of 2019. It was created by MIT Professor Silvio Micali and his team. Dr. Micali envisioned Algorand to be not just a cryptocurrency, but also a blockchain which could act as a platform and properly leverage its high security, and thus be used as a platform for smart contracts and other assets. Thus, allowing the blockchain to be integrated in a wide variety of use cases.
The Algorand protocol was developed with 3 core properties in mind:
1. Extensive Scalability
2. High Security
3. Decentralization
In addition, the Algorand blockchain was programmed to allow for rapid transactions, low fees and being a carbon-negative blockchain. Do you remember the aspects I previously brought up in our "Blockchain Book Metaphor"? These are the main points of contention where blockchain developers struggle to find an optimal solution. Well, Dr Micali et al really outdid themselves on this matter, because they managed to develop a protocol that achieves all of that. Keep on reading if you want to know how they did it.
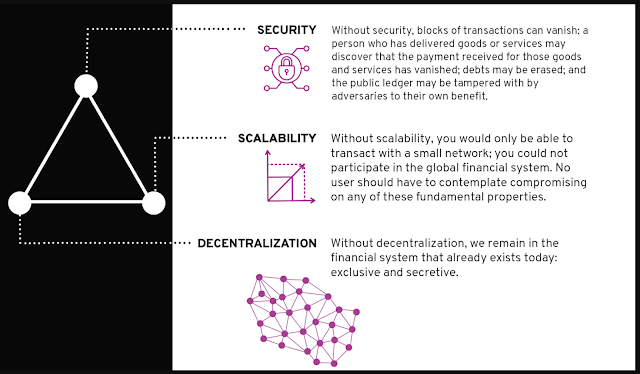 |
| The 3 core properties of Algorand (Source: Algorand.com) |
How Does Algorand Work?
Algorand works by using a method known as Pure Proof-of-Stake (Pure PoS). The logic of Pure PoS is quite straightforward - it assumes honesty from the majority of participants and makes it impossible for a minority of ill-willed people to misuse the system. This is how the Algorand developers explains it in-depth in their own blog post. I'll talk more about that further below.
In a nutshell Pure PoS works like this:
1. In a 1st phase a single Algorand token (ALGO) is randomly selected. The owner who has this token in his wallet will be the one who proposes the next block.
2. In a 2nd phase there are 1000 tokens (and their owners) that are (again) randomly selected to be a part of a "phase-2 committee". This committee are the ones who have to approve the proposed block from the 1st phase.
Benefits of Pure Proof-of-Stake
The 2nd phase allows for a highly secure system, any ill-intended 1st phase user will be declined, and the 2nd phase users being randomly selected (1000 tokens out of 10 billion), there would need to be more than 50% collaborating dishonest token-owners being randomly chosen for the same block to have any chance of ill-tampering. I'll remind you that it's a 1 out of 10 million chances for a token to be selected the first place. So, by assuming the honesty of the majority, it provides an almost surprisingly secure system.
Why? Because first off, most people are honest, and it's even difficult to conceive an environment where the majority are ill-willed and ready to cooperate. Additionally, anyone owning a sizable amount of ALGO would be doing financial harm to themselves by breaking the system, and thus risk a financial collapse of the system itself. Again, to even theoretically have a chance of tampering with the system there would need to be several billions of ALGO's at play. You're probably not looking to reduce of your portfolio value by 99% if you own that much Algorand.
The Algorand Blockchain - Technical Specs
As for some technical specifications - A new block is chosen at least every 4.5 seconds, and every chosen participant is rewarded with a certain amount of ALGO's. Since February of 2022 the passive staking reward program was phased out in benefit of the Governance Program.
Algorands average transaction speed around is therefore less than 5 seconds (as this approximately how often a block is solved) and the network fees are fixed at 0.001 ALGOs per transaction. The total supply of Algorand is set to be 10 billion in 2023.
At the moment the Algorand protocol supports 6,000 transactions per second (TPS) but aim to support 45,000 TPS in the upcoming years.
Algorand vs Bitcoin
Below is a quick infographic pointing out the main differences between Algorand vs Bitcoin. Both tokens have their strengths and weaknesses, but overall, it's pretty clear that Algorands more recent and advanced protocol puts it far ahead of BTC. Not only does Algorand have superior transaction speeds and cheaper fees compared to Bitcoin - it also offers an ecosystem full of real-life utility and interoperability. It does all of this while being an environmentally friendly blockchain.
With that said Bitcoin did actually roll out a new update in November 2021, known as the Taproot Upgrade, which should allow BTC to offer functions similar to smart contracts. Additionally, the Lightning Network was launched, which will lower fees and increase transaction speeds.
Conclusion
That concludes this quite lengthy article on the Algorand Blockchain and it's technology. It can be a pretty difficult topic to understand, nonetheless we hope our explanation was somewhat easy to follow. Hopefully you've gained insight both into how cryptocurrencies and blockchain in general work, but also learned more about the technical specifics of Algorand vs Bitcoin.
There are of course other next generation blockchains (Ethereum, Cardano, etc.) which are technically more competitive with Algorand, however comparing those will be a post for another time. Meanwhile, check out any of the other Algorand articles we've posted.
Stay educated.














0 Comments